Insulin is a hormone secreted by group of cells; islets of Langerhans within an endocrine gland called Pancreas. The gland is an organ located behind the stomach and has many other functions apart from insulin production. Pancreatic gland is responsible for the production of hormones and digestive enzymes that help in digestion process and absorption of carbohydrates from the bloodstream. Post digestion, carbohydrates are absorbed into the bloodstream increasing the sugar levels. In response to the raise in blood sugar levels, pancreas secretes insulin which binds with the insulin receptors located on the body cells thus activating the absorption of glucose from bloodstream.
Structure of Insulin:
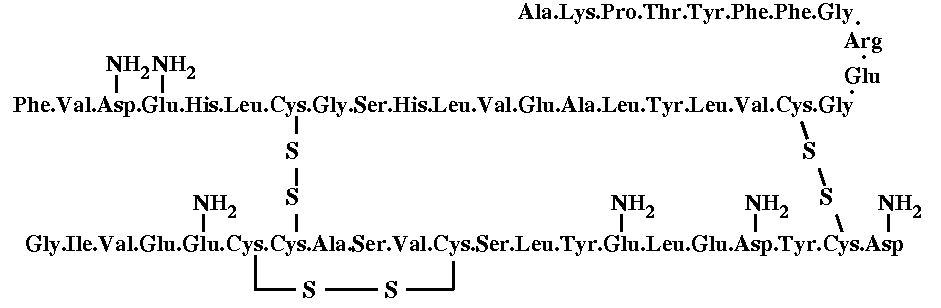
Like many hormones, insulin is also a protein with molecular weight of 6000 Dalton, consisting of two peptide chains namely “A-chain” and “B-chain”. A-chain is composed of 21 amino acids and B-chain; 30 amino acids. Both the chains are interlinked with two disulphide bonds and a disulphide bond is present within the A-chain. Below is the chemical structure of human insulin.
Route of administration:
Insulin is naturally produced by Islet cells of Pancreas. But people with Type-I Diabetes cannot produce insulin and need to take it externally. Being a protein, it is easily digestible if administered through enteral route and reaches stomach. The widely accepted route of administration is sub-cutaneous insulin injections. Injection takes time, interrupts daily schedules and is considered unpleasant by many people. Children or adolescents who require daily insulin injections may find that the regimen impacts on their daily lifestyle to an even greater degree. Hence, the researchers have developed alternative routes of administration for insulin. The ultimate goal in delivering the insulin to a patient is it has to reach the bloodstream intact.
The alternative routes of administration include nasal, mouth, lungs. All these delivery systems are not up to the mark in delivering the insulin into bloodstream intact. The oral insulin pills are developed to absorb the insulin through buccal means which promises the delivery of insulin intact into the bloodstream.
Oral Insulin Research:
Research is being carried on oral insulin pills and capsules for their safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamic parameters. Oramed pharmaceuticals in May 2010, has reported that a trial was conducted on Type 2 Diabetic patients who were administered with oral insulin capsule against placebo and closely monitored and assessed for safety, tolerability and efficacy parameters. Oramed reports that in two thirds of the subjects analyzed, statistically significant reductions in glucose as well as C-peptide were observed. Eli Lilly & Company is also working on oral insulin research.
To conclude, oral insulin therapy is still in developing stage and extensive research is required to bring the medicine available to the patients.

